Trigeminal Neuralgia
Pain along a nerve's entire course is referred to as neuralgia. The trigeminal nerve which transmits sensation from your face to your brain is impacted by the chronic pain disorder known as trigeminal neuralgia. Thus trigeminal nerve disease is characterized by excruciating pain shooting or jabbing pain that is brought on by light facial stimulation along the trigeminal nerve's path on one side of the face.
Overview
Everyday activities like eating talking and shaving can be excruciating for those who suffer from trigeminal neuralgia (TN) causing jolts that feel like electric shocks and burning or aching in the face. Severe pain attacks can occur even when you're outside in a windy environment. A rare neurological disorder called produces excruciating persistent facial pain.
What is a trigeminal nerve?
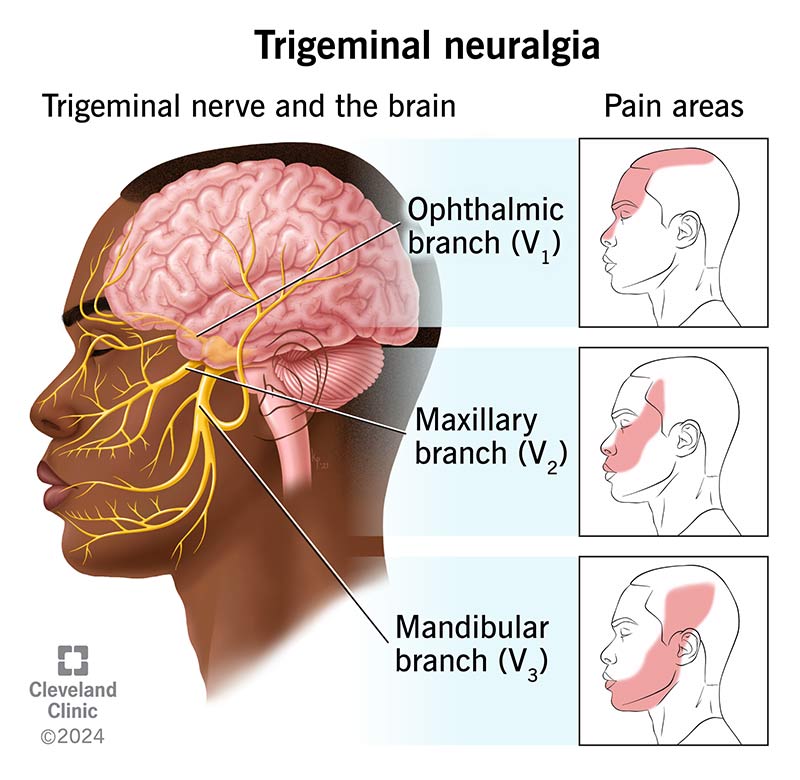
The trigeminal nerve is the 5th of the cranial nerve. Its branches cover your head and face and it grows from the brainstem. The trigeminal nerve consists of three branches:
The ophthalmic nerve: This sensory nerve branch covers the scalp and upper part of the face including the eye eyelids and forehead and carries sensation to the brain.
The maxillary nerve: This branch covers the middle of the face and is solely a sensory nerve. It transmits sensations from the nose cheeks lower eyelids upper lip gums inside of the mouth the palate upper jaw teeth and sinuses.
The mandibular nerve: There are sensory and motor components to this branch of the trigeminal nerve. It transmits feelings from your lower face encompassing the gums lower lip and jaw. It conveys senses from the front of your tongue that are not related to taste. The muscles used for swallowing biting and chewing are managed by the motor portion of this nerve.
The condition is classified into two types: TN type 1 (TN1) characterized by attacks of intense stabbing pain affecting the mouth cheek nose and/or other areas on one side of the face. TN type 2 (TN2) is characterized by less intense pain but a constant dull aching or burning pain.
Causes
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) affects twice as many women as men and is most common among people over the age of 50.
While some TN cases run in families the majority are not hereditary. When a blood vessel compresses the trigeminal nerve at the base of the brain, pain occurs.
Trigeminal neuralgia can also develop from illnesses like multiple sclerosis or damage to the nerve's myelin sheath.
Trigeminal nerve damage results from trauma to the nerve. either damage to the nerve or tumors pressing on it. This condition can also be brought on by stroke.
Symptoms
There are several ways that pain from trigeminal neuralgia can manifest.
The classic symptoms are 20-second bursts of sharp throbbing shock-like pain that are frequently brought on by contact with the face.
Patients who experience these symptoms frequently experience weeks or even years without any pain during remission periods.
Some sufferers of the illness have less intense but more persistent pain that lasts longer and is more widespread.
It's frequently described as feeling scorching.
The typical symptoms include facial pain lasting a few minutes to hours primarily on the gums teeth cheek and jaw area resembling an electric shock pain while brushing talking laughing etc.
Ayurvedic View
snayu gata vata - Due to following of nidana (causes) that aggravate vata dosha, this vikruta prakupita (aggravated), vyana vata dosha takes sthana samshraya (settles in),snayu (which is connected to motor movetments), which causes twitching pain in face, which can cause difficulty in performing day to day activities, this disease is trigeminal neuralgia. Ayurveda way of approach is to bring dosha back to prakruta awastha (balance state) in guna (quality), sthana (place), karma (function), reduce the symptoms and help to rehabilitate the affected part by ayurvedic panchakarma treatment and prevent the reoccurrence.
Ayurvedic Treatments
Snehapana Nasya Pinda sweda Shiroabhyangam Shirodhara Shiro pichu Talam Basti Gandusham
Naturopathy Treatments
Enema Mud therapy packs Acupuncture Moxibustion Manipulative therapy Diet therapy Clinical Yoga Cyclic meditation Mind sound resonance technique Pranayama Electrotherapy and Exercise therapy Reflexology
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Treatment for
DISCLAIMER: Listed treatment details are only for information purposes. Treatments and duration may vary depending on numerous factors. Treatments for your condition may not be limited to this list.






















