Uterine Prolapse
The uterus (womb) is a muscular structure maintained together by pelvic muscles and ligaments. If these muscles or ligaments stretch or weaken they can no longer support the uterus resulting in prolapse.
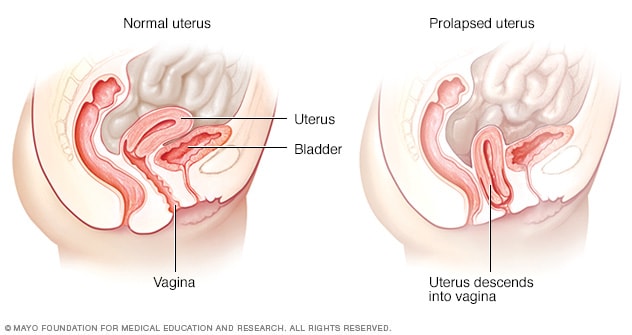
When the uterus sags or slips from its usual position and into the vagina (birth canal) this is referred to as uterine prolapse.
Overview
Uterine prolapse can be either incomplete or complete. An incomplete prolapse occurs when the uterus sags into the vagina only partially. When the uterus falls so far down that some tissue protrudes outside the vagina this is referred to as a complete prolapse.
Uterine prolapse has four stages:
Stage I: Your uterus enters the upper portion of your vagina.
Stage II: Your uterus enters the lower portion of your vagina.
Stage III: Your uterus protrudes from your vaginal opening.
Stage IV: Your entire uterus slips outside of your vagina.
Other disorders that are frequently related to uterine prolapse include,
Cystocele: a herniation (or bulging) of the upper front vaginal wall in which a portion of the bladder protrudes into the vagina. It's also known as a prolapsed bladder. This might result in urinary frequency urgency retention and incontinence (urine loss).
Enterocele: A herniation of the upper rear vaginal wall in which a tiny part of the colon bulges into the vagina. Standing causes a dragging sensation and backache which is reduced by lying down.
Rectocele: A herniation of the lower rear vaginal wall into which the rectum bulges. This makes bowel motions difficult and you may need to push on the inside of your vagina to empty it.
Causes
A combination of muscles and ligaments (pelvic floor muscles) hold your uterus in place within your pelvis. When these components deteriorate your uterus is unable to maintain its position and begins to sag. Several factors can contribute to pelvic muscle weakness including:
Menopause-related loss of muscular tone.
Pregnancy.
Vaginal childbirth is preferable especially if you've had multiple infants or newborns weighing more than 9 pounds.
Obesity.
Coughing or straining regularly.
Constipation that lasts a long time.
The heavy lifting was done repeatedly.
Symptoms
Symptoms could include,
Pelvic or vaginal pressure or heaviness
Sexual intercourse problems
Urine leakage or an impulse to empty the bladder
Low back pain
Bulging uterus and cervix into the vaginal opening
Recurring bladder infections
Bleeding in the cervix
Vaginal discharge has increased. When you stand or sit for an extended period your symptoms may worsen.
Exercise or lifting may also aggravate discomfort.
Ayurvedic View
Maha yoni- Main predominant dosha is vata dosha. Causes specific like performing of coitus in uneven bed, there is vata aggravation, this affects the yoni (uterus, vagina- female reproductive organ) then causes asamvutha mukha or ati vivrutha yoni (dilation) of the yoni (vaginal orifice) leads to mamsa utsanna (muscular protuberance in the vagina) etc, this is uterine prolapse. Ayurveda way of approach is to bring dosha, which can be vata dominant pitta and kapha dosha involvement back to balance state, strengthen the supporting structures and correcting the deformity and other symptoms by ayurvedic panchakarma treatment and treatment done for vagina (uterus-help in regain the normal position).
Ayurvedic Treatments
Prakshalanam Dhoomanam Lepanam Pichu Uttravasti Vasti Abhyangam Pinda swedam
Naturopathy Treatments
Hip bath Immersion bath Enema Packs Manipulative therapy Diet therapy Clinical yoga Exercise therapy
Uterine Prolapse
Treatment for
DISCLAIMER: Listed treatment details are only for information purposes. Treatments and duration may vary depending on numerous factors. Treatments for your condition may not be limited to this list.






















